
AWG value - influence on signal transmission
The wire diameter, i.e. the "thickness" of a wire within a data cable, has a direct influence on the quality of the data that is transported through the respective cable.
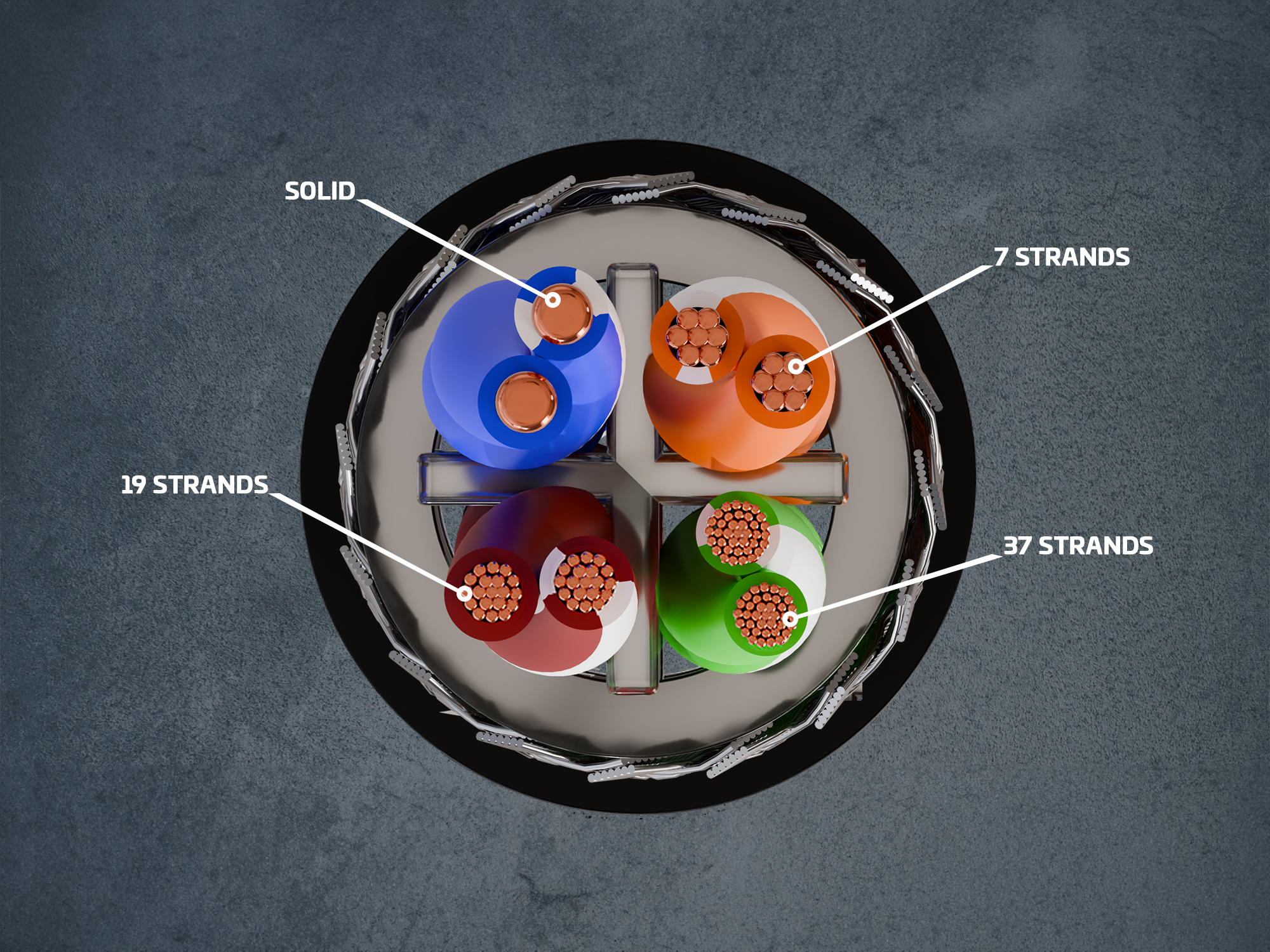
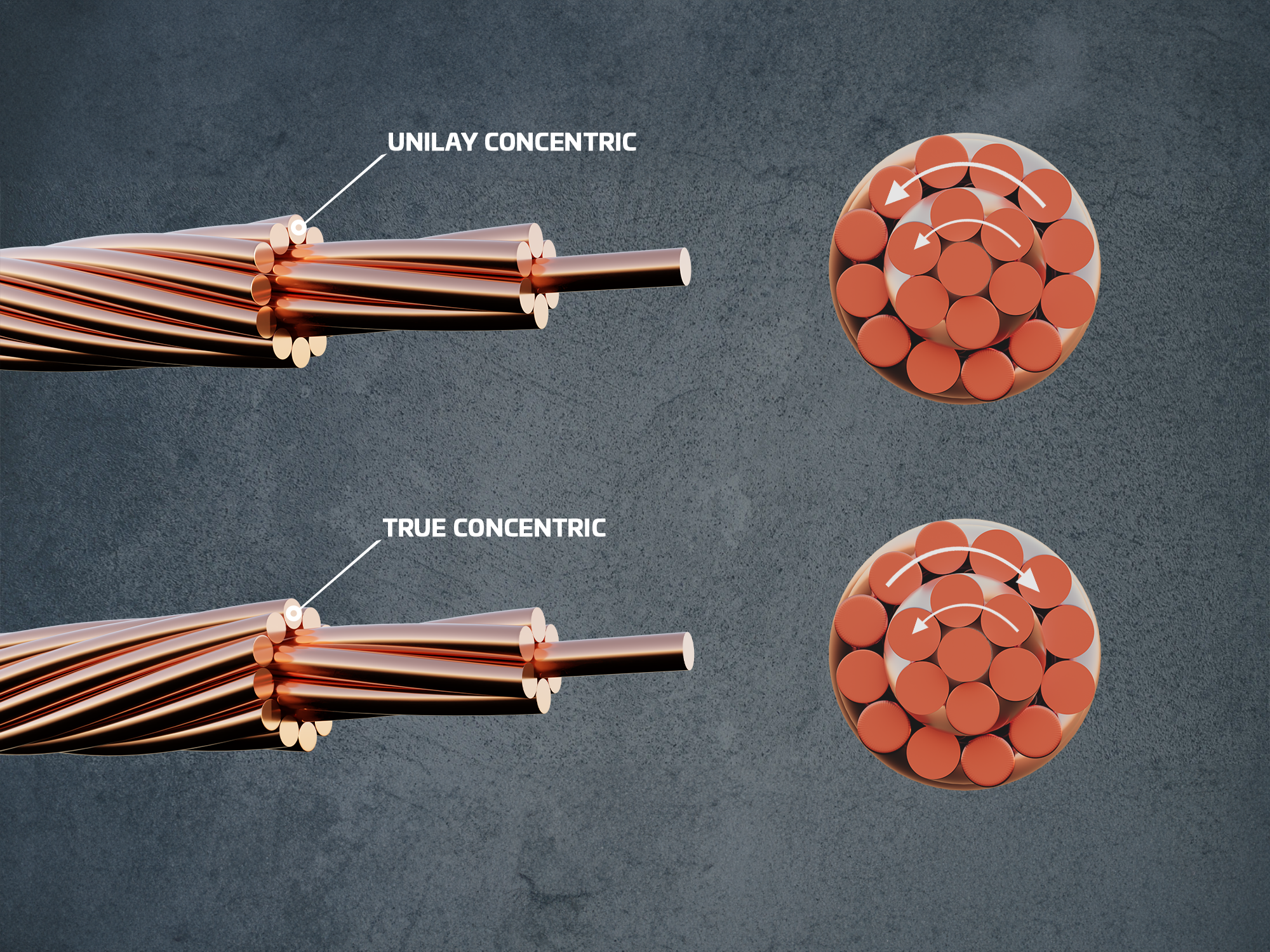
A total wire usually consists of several strands, whereby a strand in turn consists of several individual wires (in exceptional cases also of a single wire). In cable technology, 7- and 19-wire strands are generally used for data cables. The exact arrangement of the individual wires provides a regular surface and a consistent diameter of the strands. Data cables are referred to as having a concentric strand structure, i.e. the individual wires are arranged around the inner core wire in a precisely defined manner.
To define the diameter and cross-section of electrical conductors (both of single wires as well as stranded wires), the so-called AWG value comes into play – as to that, see www.cordial-cables.com/en/awg .
As a general rule, the smaller the AWG value, the thicker the wire. Hence, the AWG value of a cable has a direct influence on the data quality. This is reflected in the following factors in particular:
- Attenuation: lower AWG values (i.e. thicker wires) tend to have lower attenuation properties. This means that the data signal can be transmitted more effectively over longer distances without being severely attenuated. Accordingly, lower attenuation is essential to maintain the required signal quality (especially over longer transmission distances).
- Resistance: Cables featuring a lower AWG value generally have a lower electrical resistance and lower resistance values mean less loss of electrical energy during transmission. For that reason, lower resistance values result in a more efficient signal transmission and contribute to improved data quality.
- Flexibility: a thicker wire (= lower AWG) can cause stiffer cables and thus a reduction in flexibility. For certain application scenarios, especially as regards moving connections or patch cables, a higher flexibility may be needed.
- Costs and space requirements: Cables featuring a lower AWG value can be more expensive due to the material required and a more complex production process. Moreover, a thicker wire requires more space, a fact that should be paid close attention to regarding certain installations.
We realize that, hence, when it comes to event technology, it is not feasible to speak of "better" or "worse" values in connection with a lower or higher AWG value. Instead, the choice of a cable in the matter of AWG depends in particular on which key indicators the focus is placed. So, you have to ask yourself
- "Do I need the best possible data transmission, but can I do without high flexibility because the cable will not be moved frequently, for example?"
- "Do I need to save storage or transportation space and therefore use thinner cables with a higher AWG?"
- "Am I prepared to accept any additional costs - the main issue being that the data transmission is optimal?"
Conclusion:
As is often the case, "steering a middle course" is the best solution. The Cordial Sales Team will be happy to answer any further questions.
Click here for the AWG table .
Please note: selecting the correct cable for an application requires the careful assessment of a variety of factors including AWG ratings, shielding, insulation, cable length, data class and respective application. It is crucial to take into account all factors relevant to the specific application to ensure signal integrity and the optimum system performance.
Further interesting "Cordial Knowledge" facts on the subject:
Insulator - influence on signal transmission
Shielding - influence on signal transmission
Conductor type - influence on signal transmission