
Shielding - Influence on signal transmission
There are unshielded cables ("UTP cable: Unshielded Twisted Pair") and shielded cables (both "FTP cable: Foiled Twisted Pair" and "STP cable: Shielded Twisted Pair").
Explanation of diverse shielding designs
The structural design regarding the shielding of Ethernet cables is identified by letters.
- U - Unshielded: without shielding.
- F - Foil: Shielding with foil wrapped around the wire pairs.
- S - Braid: The wire pairs are shielded with a metal braid.
There are two additional variants featuring shielded wire pairs:
- UTP - The wire pairs are not individually shielded
- FTP - The wire pairs are individually shielded with foil
Further acronyms are derived from these terms:
- U/UTP: A U/UTP cable has no shielding of the wire pairs and no shielding per individual wire pair
- F/UTP: In F/UTP cables, all wire pairs are encased in an overall foil shield, but there is no shielding for each individual wire pair
- S/FTP: In S/FTP cables, all wire pairs are protected with an overall metal braid and each individual wire pair is shielded with foil
Shielding (and its respective variants) is therefore one of the key criteria for the effective protection against internal and external interference. The more effectively a cable - and the wire pairs within the cable - is/are shielded, the lower the negative impact of interference on the movement of the respective data. BUT: the individual types of shielding also influence the flexibility of the cable. It is therefore always imperative to evaluate the weighting of the individual factors subject to the intended use.
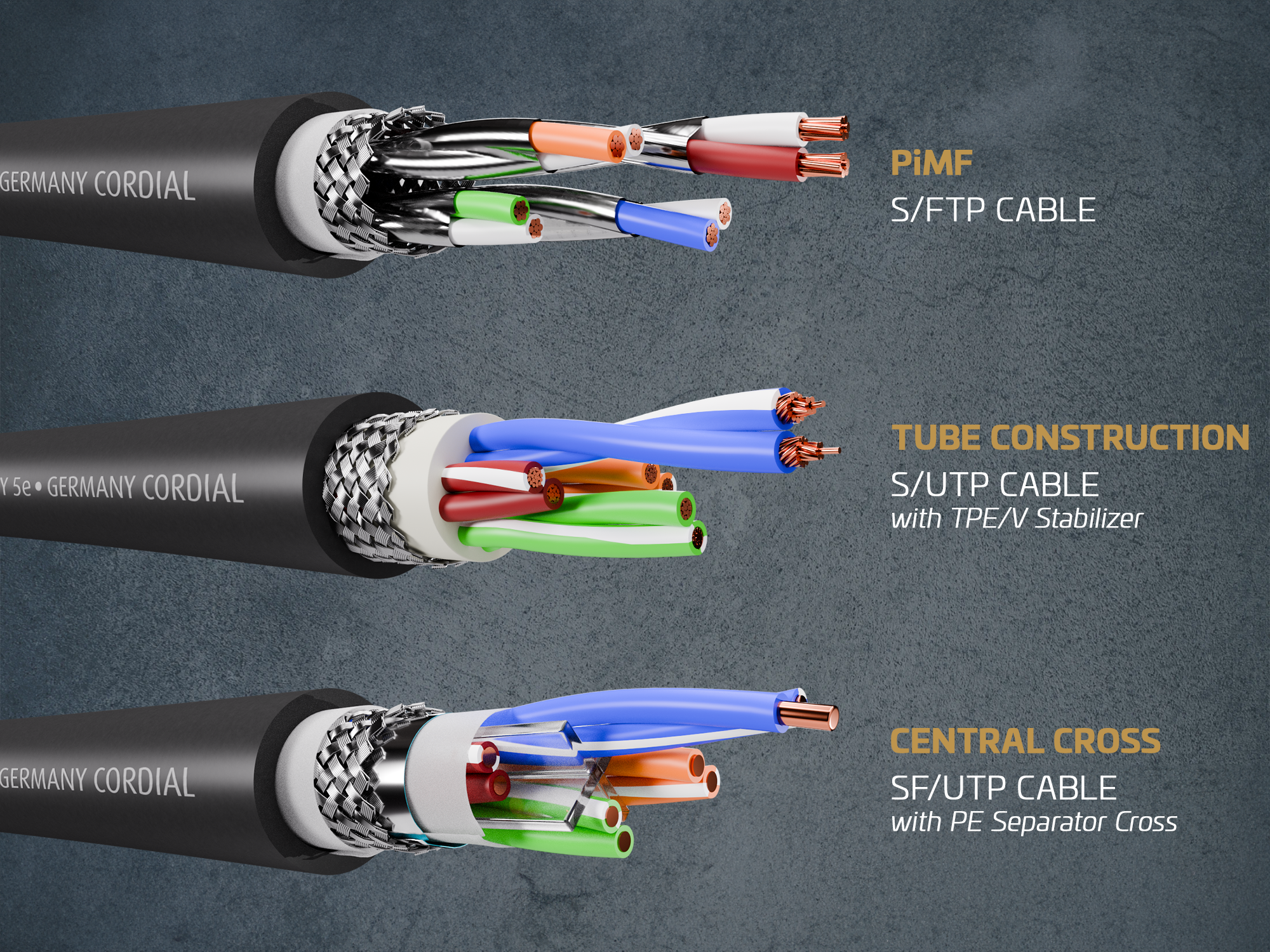
Other important terms are: PiMF, Central Cross and Tube Construction:
- PimF (pairs in metal foil): Wire pairs are individually wrapped in metal foil. This serves to shield from electromagnetic interference and improve signal integrity.
- Central Cross: This design refers to a central cross arrangement of the wire pairs in the cable. This achieves a more even distribution of electromagnetic interference.
- Tube Construction: The loose tube design helps to maintain the structure of the cable and minimizes electromagnetic interference between the wire pairs.
On the one hand, PiMF cables include SF/UTP cables (i.e. variants with shielded wire pairs - metal braiding and foil - but the wire pairs are not individually shielded from each other) and, on the other, S/FTP cables (see above, all wire pairs are surrounded by metal braiding and each individual wire pair is shielded with foil).
- CORDIAL's S/FTP cables include CCAT 6A PUR QUAD; CCAT 6A PUR LONGRUN; CCAT 7A PUR; CCAT 7A PUR LONGRUN
- The CCAT5e PUR bulk cable consists of an S/UTP cable featuring an additional stabilizer made of TPE-V (Tube Construction Cable)
- Finally, our portfolio also includes the Central Cross cables CCAT 5e PUR LONGRUN and CCAT 6A PUR, i.e. SF/UTP cables (see above) with a PE stabilizer cross.
Please note: selecting the correct cable for an application requires the careful assessment of a variety of factors including AWG ratings, shielding, insulation, cable length, data class and respective application. It is crucial to take into account all factors relevant to the specific application to ensure signal integrity and the optimum system performance.
Further interesting "Cordial Knowledge" facts on the subject:
AWG - Influence on signal transmission